In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide the term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group.
Allylic halide vs vinylic halide.
A vinylic halide from an aryl halide.
C h 2 c h 3 c c h 2 b r.
They exhibit faster s n 2 reactivity than secondary alkyl halides because the bimolecular transition state is stabilized by hyperconjugation between the orbital of the nucleophile and the conjugated pi bond of the allylic.
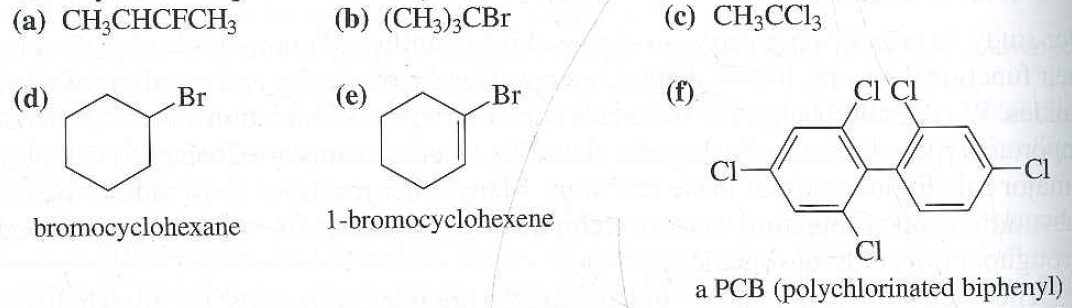
Which of the following is classified as a vinylic halide.
For this reason alkenyl halides with the formula rch chx are sometimes called vinyl halides.
Why aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides for nucleophilic substitution.
Allylic halide is a halide atom present on the carbon which is adjacent to the double bonded carbon.
Key difference allylic vs vinylic carbons functional groups are very important in understanding the different physical and chemical properties of organic molecules the terms allylic and vinyl carbons indicate whether the carbon atom is bonded directly or indirectly to a double bond in a molecule.
In high dielectric ionizing solvents such as water dimethyl sulfoxide acetonitrile s n 1 and e1 products may be observed.
In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon.
Other articles where vinylic halide is discussed.
They are subdivided into alkyl vinylic aryl and acyl halides.
Both groups own a double bond between two carbon atoms where all the other atoms are bonded through single bonds.
S n 2 reactions of allylic halides and tosylates.
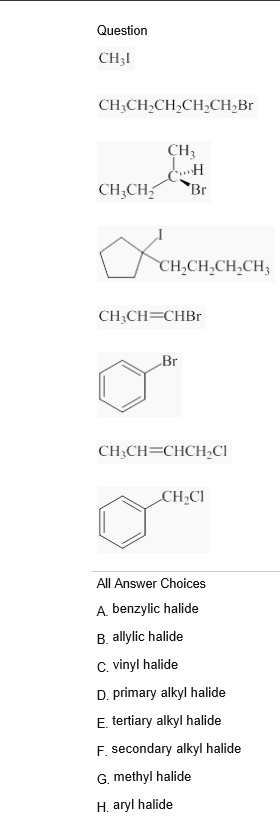
Ch 3ch chch 2cl ch 3ch choh ch 3ch 2ch 2ch 2br brch 2ch ch 2 ch 3ch chcl what general classification is given to the molecule below.
Allylic halides and tosylates are excellent electrophiles for bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reactions s n 2.
Rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º.
A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond.
In alkyl halides all four bonds to the carbon that bears the halogen are single bonds.
Key difference allyl vs vinyl both allyl and vinyl groups have slightly similar structures with a small variation.
In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of.
Allyl groups have three carbon atoms and five hydrogen atoms.
Allyl h 2 c chch 2 rapid s n 2 substitution for 1º and 2º halides.
The key difference between allylic and vinylic carbon is that allylic carbon is the carbon.
The key difference between these two structural components is the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Identify the number of allylic and vinylic protons in a molecule 001 duration.
From the perspective of applications the dominant member of this class of compounds is vinyl chloride which is produced on the scale of millions of.
Formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom.
For 3º halides a very slow s n 2 substitution or if the nucleophile is moderately basic e2 elimination.
Primary chloride secondary chloride tertiary chloride vinyl chloride benzyl chloride provide the name of the bromoalkane shown below.